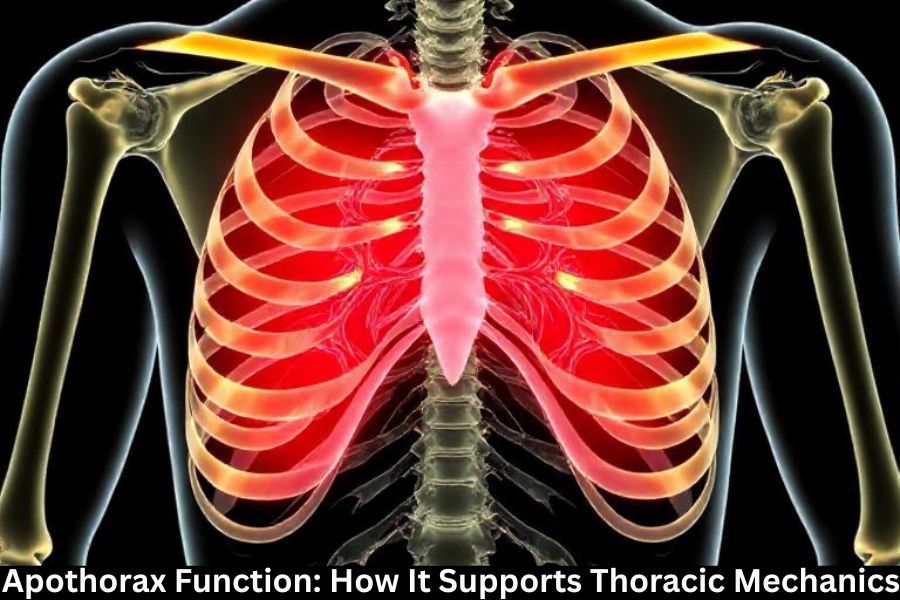
In the intricate world of human biomechanics, even the smallest structures play vital roles in our day-to-day functioning. One such structure is the apothorax—a term that’s less familiar to most, but one that plays a significant part in the mechanics of the thoracic region. But how exactly does it support thoracic mechanics? Let’s explore the anatomy, function, and importance of the apothorax in maintaining proper thoracic movement.
What is Apothorax?
The apothorax refers to a specific region or structure within the thoracic cavity, which is the part of the body encased by the ribcage. While the term is not universally known, it essentially refers to the dynamic interaction between the thoracic spine, ribs, and connective tissues, working together to facilitate efficient breathing and movement. Apothorax helps the ribcage expand and contract with each breath, contributing to the fluid movement of the chest.
Anatomy of the Thoracic Region
To understand the apothorax’s function, we first need to know the anatomy of the thoracic region. The thoracic cavity is surrounded by the ribs, sternum, and vertebral column. The thoracic spine, which houses the ribs, plays a crucial role in movement and support, while the diaphragm separates the thoracic and abdominal regions and aids in respiration. The ribs provide structure and protection for vital organs like the heart and lungs, while also allowing for flexibility during breathing.
The Role of Apothorax in Thoracic Mechanics
So, how does apothorax fit into this puzzle? Essentially, it ensures that these different parts of the thoracic cavity move in harmony. Apothorax acts as a bridge between the spine and ribs, allowing the chest to expand and contract smoothly with the respiratory process. This interaction enables efficient thoracic movement, making it easier for the body to adapt to changes in posture or physical activity.
Apothorax and Respiratory Function
One of the most vital functions of the apothorax is its role in respiration. When you inhale, your diaphragm contracts, and the ribcage expands to allow the lungs to fill with air. The apothorax facilitates this movement by providing structural support and aiding in the proper positioning of the ribs and spine. Without proper function of this area, breathing could become labored and inefficient.
Apothorax in Postural Alignment
Another significant function of the apothorax is its involvement in postural alignment. Our spine, ribs, and the surrounding muscles work together to maintain an upright posture. Apothorax helps to stabilize the thoracic spine and ribs, ensuring that the body remains balanced, whether you’re sitting, standing, or engaging in physical activities. Proper alignment is crucial not only for comfort but also for preventing long-term musculoskeletal issues.
Movement of the Rib Cage and Apothorax
The rib cage is an extraordinary structure designed to expand and contract during breathing. But it’s not just about taking in air—these movements also enable the torso to rotate, bend, and twist. The apothorax plays a key role in facilitating these motions. By supporting the ribs and vertebrae, it ensures that the rib cage moves smoothly during physical activity, whether it’s for deep breaths or dynamic motions like lifting weights or twisting the body.
Apothorax and the Respiratory Muscles
The intercostal muscles (those located between the ribs) are essential for breathing. These muscles contract to help the rib cage expand and contract. Apothorax interacts with these muscles to support their function, ensuring that they can work efficiently during inhalation and exhalation. This relationship between apothorax and the respiratory muscles allows for optimal thoracic function.
Injuries and Disorders Affecting Apothorax Function
Just like any other part of the body, the apothorax is vulnerable to injury. Conditions like thoracic outlet syndrome, scoliosis, or herniated discs can affect the mechanics of this area, leading to pain, restricted movement, and difficulty breathing. Injuries can disrupt the smooth coordination between the ribs, spine, and diaphragm, impacting overall thoracic function.
Apothorax in Athletic Performance
Athletes rely heavily on thoracic mechanics for performance, especially when it comes to activities that require deep breathing or complex movement patterns. Apothorax plays a crucial role in ensuring that the rib cage moves efficiently, allowing athletes to perform at their best. Whether running, swimming, or lifting weights, an optimized apothorax can significantly improve stamina and overall physical performance.
Maintaining Apothorax Health
Like any part of your body, the apothorax requires proper care to function optimally. Stretching exercises, strengthening the core, and breathing exercises can improve thoracic function and prevent stiffness or injury. Regular movement and maintaining good posture are also essential for keeping the apothorax and the entire thoracic region healthy.
Apothorax in the Aging Population
As we age, the thoracic region can undergo various changes that impact its mechanics. The ribs may become stiffer, and the diaphragm can lose its elasticity. This can affect the movement and function of the apothorax, making it harder to take deep breaths or maintain an upright posture. It’s crucial for older adults to engage in activities that promote flexibility and strength in the thoracic region to maintain health and mobility.
Apothorax and Breathing Disorders
In individuals with respiratory disorders like asthma or COPD, the function of the apothorax becomes even more critical. These conditions can lead to a restricted ability to breathe deeply, and any dysfunction in the apothorax can exacerbate these issues. Proper care and rehabilitation of the thoracic region can improve breathing patterns and overall lung capacity.
Future Research Directions
The field of thoracic mechanics is still evolving, and emerging research is shedding light on the intricate functions of apothorax. With advances in medical imaging and biomechanics, scientists are exploring new ways to understand how apothorax supports movement and respiration. These studies may lead to better treatments for conditions affecting the thoracic region and help improve quality of life for many people.
Conclusion
The apothorax, though often overlooked, is a crucial component of the thoracic region that plays a pivotal role in supporting both respiration and movement. By ensuring the proper function of the ribs, spine, and diaphragm, apothorax contributes to the body’s overall flexibility, posture, and breathing efficiency. Maintaining its health is essential for optimal thoracic mechanics and overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is apothorax, and why is it important?
Apothorax is a structure in the thoracic cavity that supports the ribs, spine, and diaphragm, enabling smooth movement and efficient breathing.
Can injuries affect apothorax function?
Yes, injuries to the ribs, spine, or muscles can impair apothorax function, leading to pain, restricted movement, and difficulty breathing.
How can I improve the health of my apothorax?
Regular exercise, stretching, and good posture are key to maintaining the health and function of the apothorax.
Does apothorax impact athletic performance?
Yes, proper apothorax function helps athletes with efficient breathing and movement, which are essential for peak performance.
How does apothorax affect older adults?
As we age, the thoracic region becomes stiffer, which can affect apothorax function. Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining thoracic health in older adults.

Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.info/pt-BR/register?ref=GJY4VW8W
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://accounts.binance.com/pt-PT/register-person?ref=KDN7HDOR
w0vlaw
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.